Chromosome Duplications Often Result in Abnormal Phenotypes Because
It involves the production of more copies of a particular region. Such imbalances often disrupt large numbers of dosage-sensitive developmentally important genes and result in specific and complex phenotypes.

Question Chromosome Duplications Often Result In Abnormal Phenotypes Because A Course Hero
Chromosome duplications often result in abnormal phenotypes because.
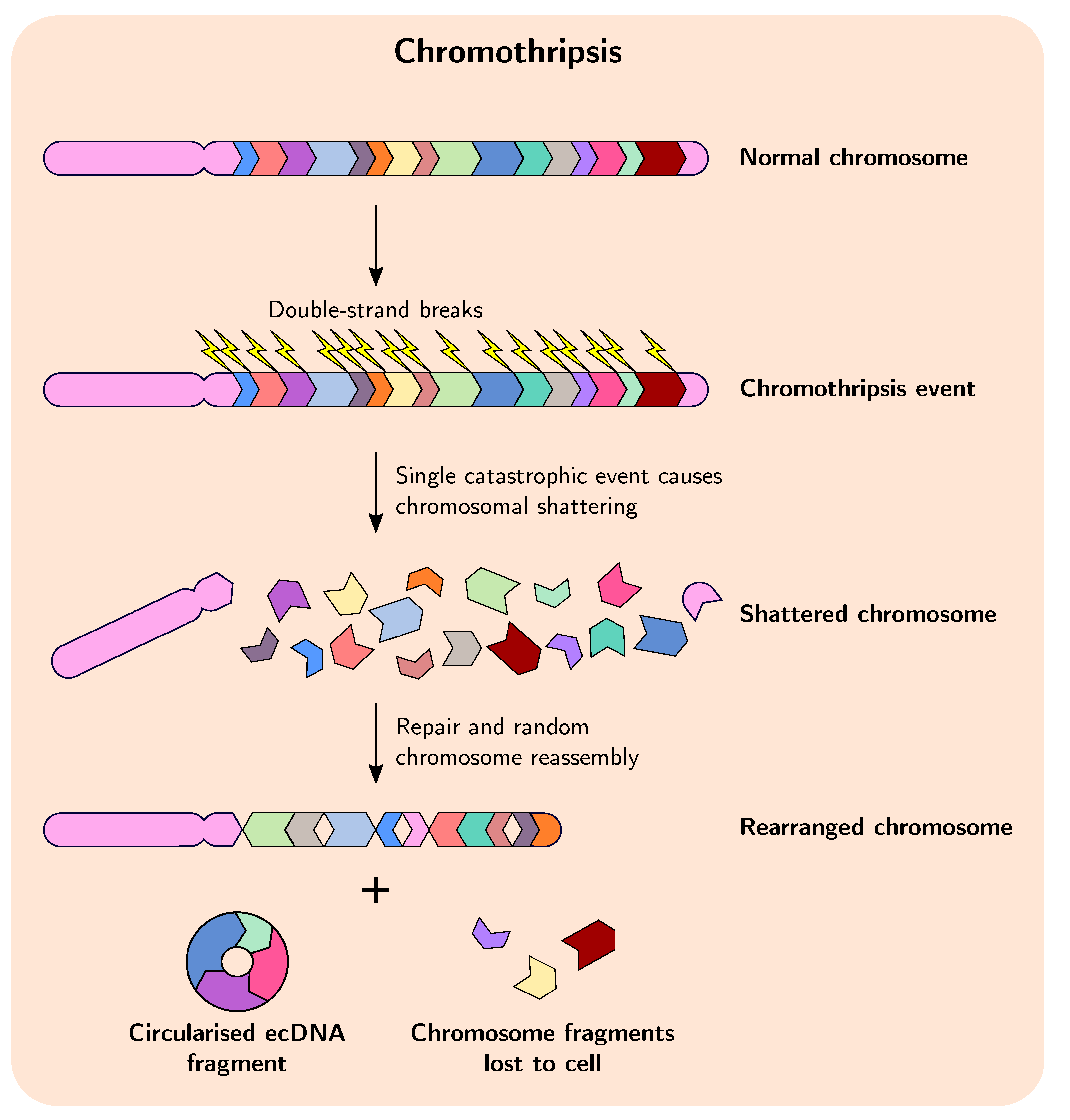
. A numerical abnormality mean an individual is either missing one of the chromosomes from a pair or has more than two chromosomes instead of a pair. Many human genetic disorders result from unbalanced chromosome abnormalities in which there is a net gain or loss of genetic material. The finding of ring chromosomes without apparent loss of genetic material in subjects with abnormal.
Developmental processes depend on the relative amounts of proteins encoded by different genes What is pseudodominance and how is it produced by a chromosome deletion. Developmental processes depend on the relative amounts of proteins encoded by different genes. Chromosome duplications often result in abnormal phenotypes because.
Solved Chromosomal Duplications Often Result In An Abnormal Chegg Com X-linked dominant disorders are uncommon relative to other types of mendelian diseases and show an excess of affected females in a family since women have two X chromosomes Fig. Rings are commonly unstable mitotically and often form double ring structures. Chromosome duplication often result in abnormal phenotypes because developmental processes depend on the relative amounts of proteins encoded by different genes extra copies of the genes within the duplicated region do not pair in meiosis.
Chromosome Abnormalities Fact Sheet. The resulting polyploid carries chromosome sets derived from two or. Question Chromosome duplications often result in abnormal phenotypes because.
Bextra copies of the genes within the duplicated region do not pair in meiosis. In some cases no deletion has been detected and the abnormal phenotype has been attributed to mitotic ring instability. Developmental processes depend on the relative amounts of proteins encoded by different genes.
Extra copies of the genes within the duplicated region do not pair in meiosis. The chromosome is more likely to break when it loops in meiosis. Extra copies of the genes within the duplicated region do not pair in meiosis.
Rings arise when two broken ends of the same chromosome fuse. In some cases no deletion has been detected and the abnormal phenotype has been attributed to mitotic ring instability. Duplications often have major effects on the phenotype possibly by altering gene dosage.
Autopolyploidy and allopolyploidy Autopolyploidy is caused by accidents of mitosis or meiosis that produce extra sets of chromosomes all derived from a single species. Large-scale duplications often result in abnormal phenotypes because. Alternately some chromosomal syndromes may be caused by a.
Ring chromosomes are often associated with abnormal phenotypes because of loss of genomic material at one or both ends. Chromosome duplications often result in abnormal phenotypes because a. Chromosome duplications often result in abnormal phenotypes because.
Developmental processes depend on the relative amounts of proteins encoded by different genes. Chromosome duplications often result in abnormal phenotypes because. Polyploidy is an increase in the number of chromosome sets.
The chromosome is more likely to break when it loops in meiosis. Duplication is a type of mutation. We investigated 33 different ring chromosomes in patients with phenotypic abnormalities by array.
And 2 the associated duplication will in general cause further phenotypic anomalies and might. Abnormal phenotypes due to the loss of material at both or at least one chromosome end. The chromosome is more likely to break when it loops in meiosis.
Group of answer choices. Usually chromosome material telomeric to the breakpoints is lost and leads to an abnormal phenotype. Chromosome abnormalities can be numerical or structural.
The max speed on this car is listed as 310 miles per hour but Bugatti has decided to design restrictions around the tires as their reason for. In individuals heterozygous for a chromosome duplication the duplicated region of the chromosome loops out when homologous chromosomes pair in prophase I of meiosis. This type of mechanism must be kept in mind when evaluating possible genotype-phenotype correlations in ring chromosomes since in these cases.
Ring chromosomes are often associated with abnormal phenotypes because of loss of genomic material at one or both ends. Developmental processes depend on the relative amounts of proteins encoded by different genes b. Allopolyploidy arises from hybridization between two species.
11 Concept Check 1 2 of 2 Chromosome duplications often result in abnormal phenotypes because a. Isochromosomes arise when one part of the chromosome is duplicated and separated from the other. 1 the deletion may be larger or smaller than first estimated based on the size of the ring with a different impact on the phenotype.
We investigated 33 different ring chromosomes in patients with phenotypic abnormalities by array based comparative genomic. The joining of two acrocentric chromosomes at the centromeres with loss of their short arms to. Adevelopmental processes depend on the relative amounts of proteins encoded by differnt genes.
Developmental processes depend on the relative amounts of proteins encoded by different genes. Extra copies of the genes within the duplicated region do not pair in meiosis. A structural abnormality means the chromosomes structure has been altered in one of several ways.
A chromosome duplication is a mutation that doubles part of a chromosome. Thus in principle the abnormal phenotypes are essentially due to haploinsufficiency of those dosage sensitive genes contained in the deleted segments. Extra copies of the genes within the duplicated region do not pair in meiosis.
View Test Prep - ch8-1 from BIOL 310 at Eastern Washington University. Extra DNA must be replicated which slows down cell division. Briefly explain why in humans and mammals sexchromosome aneuploids are more common than autosomal aneuploids.

Question Chromosome Duplications Often Result In Abnormal Phenotypes Because A Course Hero

Genetics In The News Chromosomal Mutations Chromosome Mutations

Question Chromosome Duplications Often Result In Abnormal Phenotypes Because A Course Hero

Genes Free Full Text Gene Duplication And Gene Fusion Are Important Drivers Of Tumourigenesis During Cancer Evolution Html

Question Chromosome Duplications Often Result In Abnormal Phenotypes Because A Course Hero

Question Chromosome Duplications Often Result In Abnormal Phenotypes Because A Course Hero
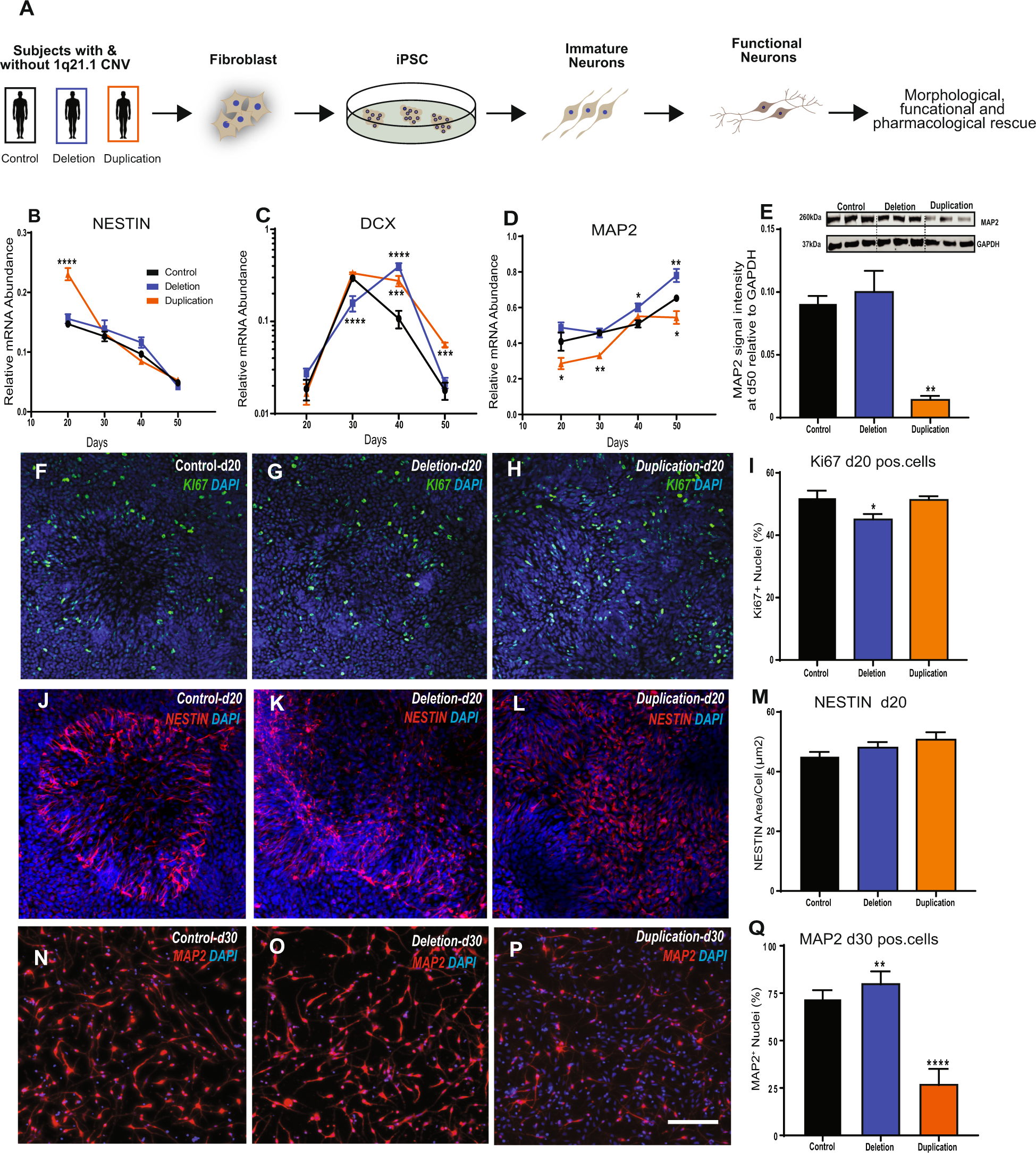
Using Induced Pluripotent Stem Cells To Investigate Human Neuronal Phenotypes In 1q21 1 Deletion And Duplication Syndrome Molecular Psychiatry
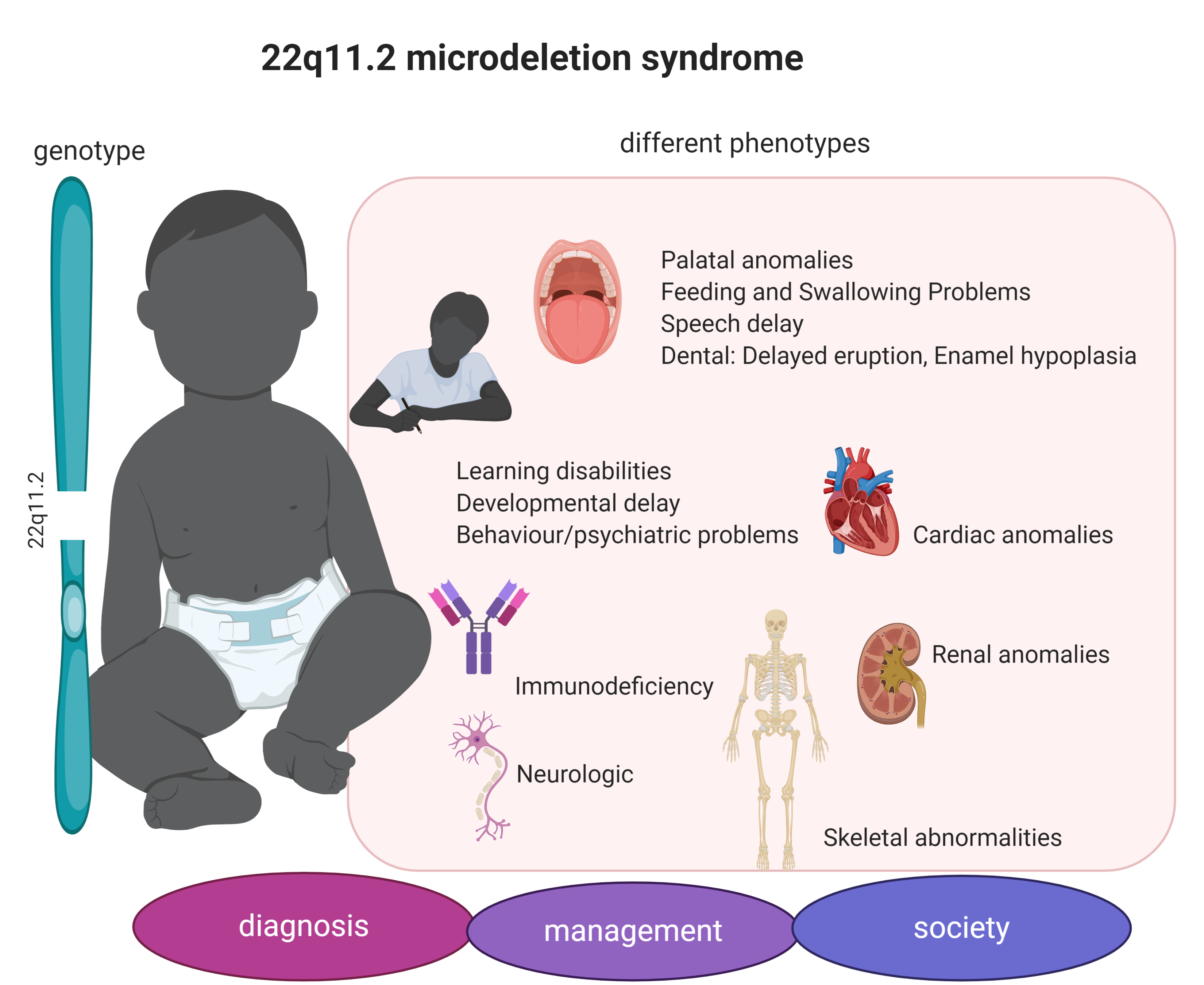
Genes Free Full Text Consequences Of 22q11 2 Microdeletion On The Genome Individual And Population Levels Html

Question Chromosome Duplications Often Result In Abnormal Phenotypes Because A Course Hero

Solved Chromosomal Duplications Often Result In An Abnormal Chegg Com

Solved Chromosomal Duplications Often Result In An Abnormal Chegg Com

Question Chromosome Duplications Often Result In Abnormal Phenotypes Because A Course Hero

Segmental Duplication An Overview Sciencedirect Topics

Hyperexcitable Phenotypes In Induced Pluripotent Stem Cell Derived Neurons From Patients With 15q11 Q13 Duplication Syndrome A Genetic Form Of Autism Biological Psychiatry
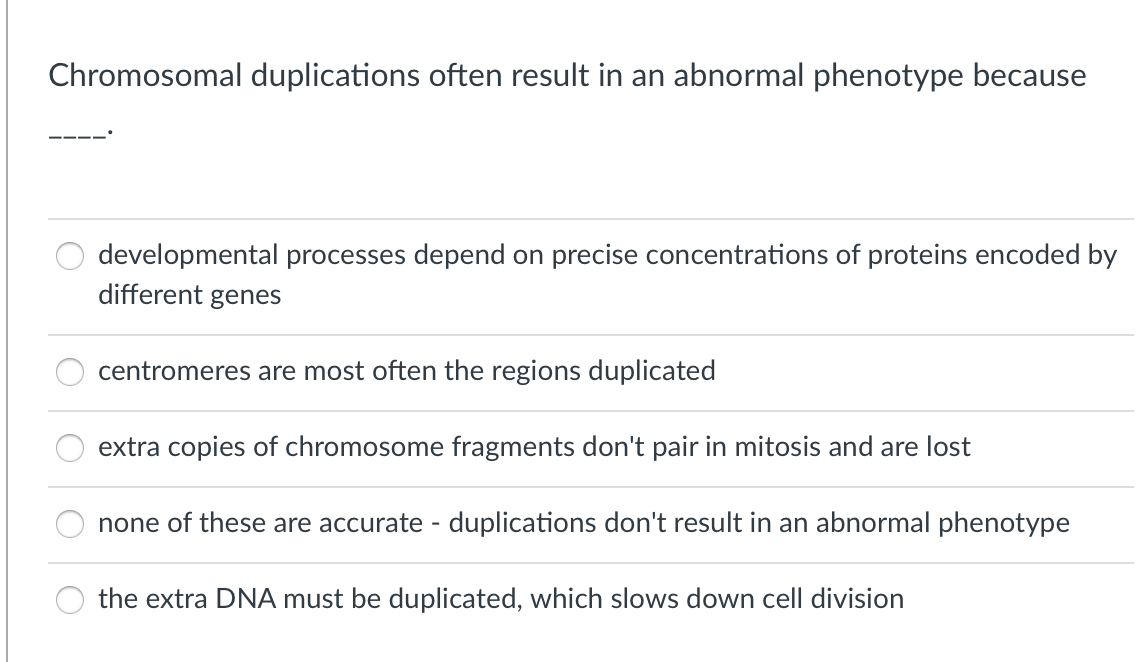
Solved Chromosomal Duplications Often Result In An Abnormal Chegg Com

Solved Chromosome Duplications And Deletions Frequently Chegg Com

Chapter 6 Chromosome Variation Flashcards Quizlet
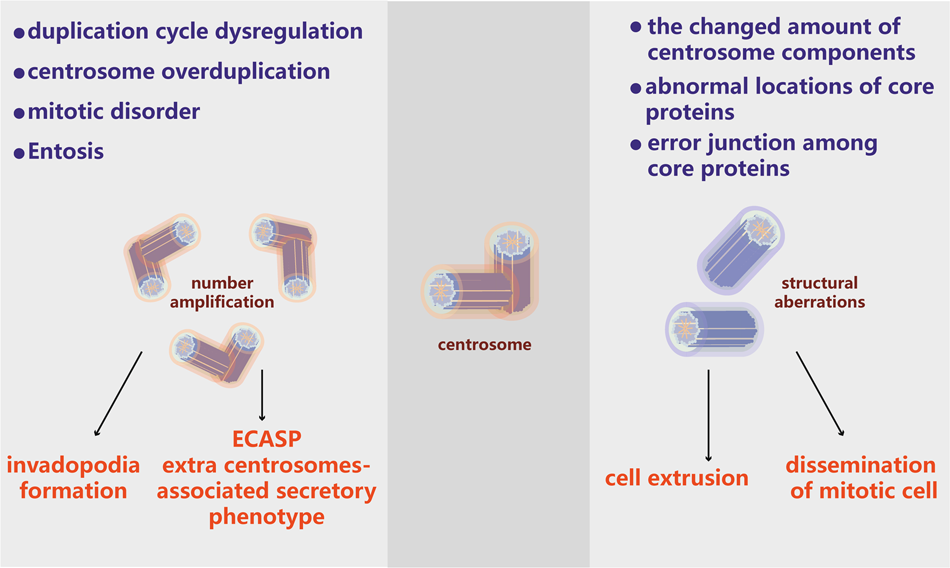
Centrosome Dysfunction A Link Between Senescence And Tumor Immunity Signal Transduction And Targeted Therapy

Solved Chromosome Duplications And Deletions Frequently Chegg Com
Comments
Post a Comment